Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a Cochlear Implant?
The cochlear implant, popularly known as the “bionic ear”, produced for people with severe hearing loss and who can no longer benefit from hearing aids, stands out as a technology that greatly improves the quality of life.
Contents
What is a cochlear implant?
In which diseases are cochlear implants used?
How is a cochlear implant applied? How is a cochlear implant inserted?
Frequently asked questions about the cochlear implant
What is a cochlear implant?
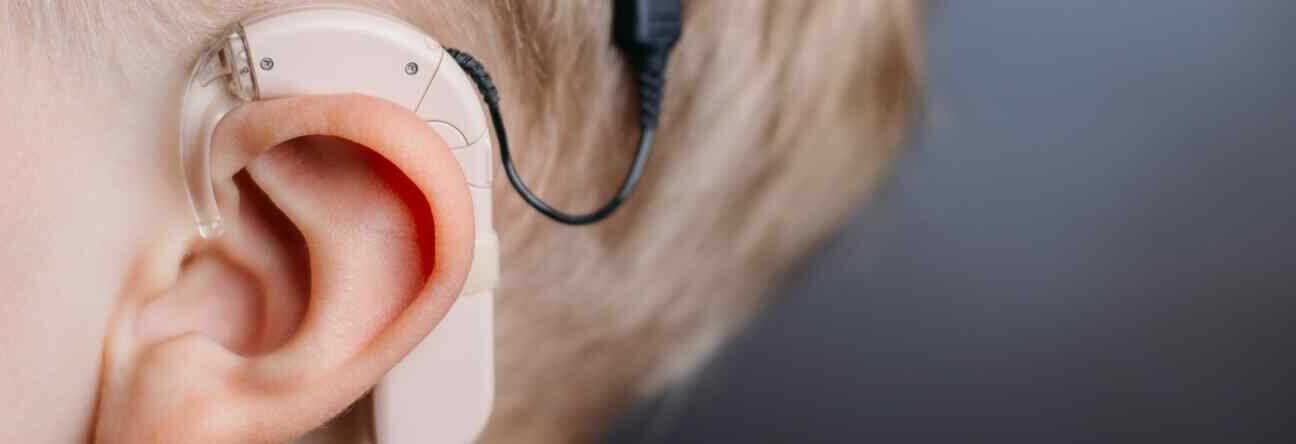
People with severe hearing problems “What is a bionic ear?” or “What is a Cochlear implant?” seeks the answer to the question. Bionic ears, that is, cochlear implants, are devices that do not benefit from hearing aids, are used in people with severe hearing loss in both ears and are surgically placed. It is also known as the bionic ear among the public. Thanks to these devices, it is possible for patients to perceive sound. So a cochlear implant is an electronic device that improves hearing. It is a good option for people who cannot hear well and have severe hearing loss, and patients can regain hearing with bionic ear surgery.
Unlike hearing aids, the cochlear implant passes through the damaged parts of the ear to transmit a sound signal to the auditory nerve. Cochlear implants use a sound processor that sits behind the ear. This processor captures the audio signals and sends them to the receiver, which is placed under the skin behind the ear. This receiver sends the signals to the electrodes placed in the inner ear, known as the cochlea, that is, in the ‘cochlea’ region of the ear. Signals also stimulate the auditory nerve, these signals are directed to the brain. The brain also interprets signals as sounds, but these sounds are not exactly natural sounds. Learning to interpret signals from a cochlear implant takes some time and training. Most people with cochlear implants achieve significant gains in speech and hearing between 3-6 months of use.
In which diseases are cochlear implants used?
Cochlear implants can improve hearing in people with severe hearing loss who no longer see the benefit of using hearing aids. Cochlear implants can improve their communication and thus their quality of life. Cochlear implants can be placed in one ear (unilateral) or in both ears (bilateral). Adults will usually initially have a cochlear implant and a hearing aid. Later, as the hearing loss progresses in the ear in which the hearing aid is used, it may switch to two cochlear implants. Cochlear implants are often placed in both ears at the same time, especially in infants and children learning to speak, in children with severe bilateral hearing loss. Those who use cochlear implants generally state that they are satisfied.
How is a cochlear implant applied? How is a cochlear implant inserted?
A cochlear implant consists of some parts. This device is also known as ear implant or implant ear. A microphone that picks up ambient sound, a speech processor that selects and regulates the sounds picked up by the microphone, a transmitter and receiver/stimulator that receives signals from the speech processor and converts them into electrical pulses can be counted as parts of the cochlear implant. There are many different models of cochlear implants on the market. An electrode array, the microphone, which is a group of electrodes that collects electrical sounds from the stimulus and sends them to different parts of the auditory nerve, is located behind the ear. The sound processor also sits just above the microphone. The electrode part is surgically placed in the cochlea region of the ear. The operation is also known as hearing implant surgery. General anesthesia is performed in the operation part. The Otorhinolaryngology Specialist makes an incision behind the ear of the patient to be operated. At this point, the mastoid bone is parted. After this incision, the electrodes of the cochlear implant device are placed in the cochlea area and the incision is closed. Nausea, dizziness and discomfort in the ears may occur after cochlear implant surgery, but these are temporary. The inserted cochlear implant is not immediately activated. It is usually activated between two and six weeks after surgery. The duration of the operation may vary according to the patient’s condition. An implant will not restore normal hearing. Cochlear implants can give people with impaired hearing a useful representation of ambient sounds and help them understand speech. In the post-bionic ear surgery process, it would be right to apply what the doctor says and act according to his directions.
Apart from the way the surgery is performed, another issue that is curious about the cochlear implant is the cochlear implant prices. Cochlear hearing aids prices vary according to need, brand and model. Ear implant prices also vary according to the patient. In other words, cochlear implant device prices can be determined according to the patient’s condition and needs. The price of cochlear implant surgery also varies according to the condition of the person to be applied. Regarding the price of bionic ear surgery, it would be appropriate to apply to the hospitals that perform bionic ear surgery and be examined and evaluate the process there.
Frequently asked questions about the cochlear implant
What is a middle ear implant?
Devices placed in the middle ear in patients with outer and inner ear problems, who cannot use hearing aids or who cannot benefit from hearing aids, are called active middle ear implants. In other words, it is the other name of the cochlear implant.
What is bionic ear surgery? What is cochlear implantation?
Cochlear surgery, ear implant surgery are also called bionic ear surgery.
What are the benefits of a cochlear implant?
Those who have cochlear implants can hear speech without the need for visual cues such as lip-reading, they can recognize everyday environmental sounds, they can acquire the ability to listen in a noisy place, they can detect where the sound is coming from, they can comfortably watch and listen to television and hear phone conversations.
At what age is a cochlear implant done? At what age is bionic ear surgery performed?
It can be applied to anyone, from children with congenital hearing loss who cannot speak, to elderly patients, depending on the situation.
Who can have a cochlear implant?
People whose verbal communication is interrupted, those who have limited or no benefit from hearing aids given with special hearing tests, those who can provide motivation to participate in hearing rehabilitation, and those who have realistic expectations from cochlear implant are suitable for in-ear hearing aid surgery.
What is a pediatric cochlear implant?
The pediatric cochlear implant device is also used for children with severe hearing loss. It does not have a different principle with the cochlear implant in adults. It can be easily applied to children who are deaf or have severe hearing difficulties. According to the latest figures, as of December 2019, hundreds of thousands of devices have been implanted worldwide. According to the FDA alone in 2019, approximately 118,100 devices were implanted in adults and 65,000 in children in the United States. Approved by the FDA in 1980, the cochlear implant can also be used in children under 12 months of age since 2000. Studies have also shown that when children younger than 12 months of age have a cochlear implant and then receive intensive therapy, they can hear, understand sounds and music, and speak better than their peers who get implants as they grow up. Research also reveals that eligible children who receive a cochlear implant before 18 months of age develop language skills at a comparable rate to children with normal hearing.
What is the cochlear implant process like?
Surgically implanted hearing aids – which can also be heard in the public as brain-implanted hearing aids – mean that the use of a cochlear implant requires both a surgical procedure and substantial therapy to learn or regain hearing for the first time. Not everyone performs at the same level with ear implant devices. The decision to have a cochlear implant should include discussions with a variety of medical professionals, including an experienced cochlear implant surgeon. Some people may choose not to have a cochlear implant for various personal reasons. As with any surgery, surgical implants are almost always safe, although complications are a risk factor. It will also take time to learn the sounds created by the cochlear implant, that is, the bionic hearing aid. Speech-language pathologists and audiologists are often involved in this learning process. Before the implantation procedure, all these factors need to be considered. Cochlear implant users are pleased to regain their hearing after this process. In addition, cochlear implant models vary by brand. It is also possible to obtain information on this subject from the physician.
What is cochlear? What is Cochlear?
Cochlear means nothing by itself. It is a word derived from cochlea. The cochlea is also defined in medicine as the auditory part of the inner ear. It is a phenomenon located inside the inner ear, which can also be defined as a snail because its shape resembles a spiral. The cochlea converts sounds into signals. These signals are transmitted to the brain by the auditory nerve so that hearing is provided. The cochlea is important for hearing.
What are the risks of cochlear implant surgery?
Cochlear implant surgery is a safe and well tolerated procedure when performed by specialists and in a healthcare facility where all conditions are available. Rarely, as with all surgeries, some risks may arise, including the following. Bleeding, swelling, infection at the implant site, ringing in the ear, numbness around the ear, dizziness, change in mouth taste, dry mouth are among the mild risks. Risks such as facial nerve injury, spinal fluid leakage, meningitis may also occur when performed in inappropriate places and by non-experts. Other risks may occur depending on the patient’s medical condition.
What happens after cochlear implant surgery?
Putting an implant in the ear and after is a serious process. When leaving the hospital, patients are instructed on how to care for the incisions. Patients are also taught how to change dressings and check stitches. A follow-up appointment should be made about a week later or at activation to examine the incisions and remove the stitches. It is necessary to inform the doctor in case of increasing pain, discharge or fever after the procedure. After the initial surgery, you will have some time to heal before the implant device is opened or activated. About four to six weeks after surgery, the outer portions of the cochlear implant will be added. These include a microphone and speech processor. At that time, the speech processor is programmed and activated, causing the internal device to stimulate the cochlear nerve in response to sounds. In addition, the basics of use and care of the implant are taught to the patient. For the adjustments, the patient comes to the hospital in a few months and is informed about the fine adjustments made by the experts. Learning to use a cochlear implant is a gradual process. It will likely also require visits with speech-language pathologists and audiologists. However, thanks to the cochlear implant, the quality of life of those who have hearing problems will increase even more.
What is the difference between a cochlear implant and a hearing aid?
The difference between implant and hearing aid is a curious subject. Bionic ear and hearing aid are different from each other. The difference between cochlear implant hearing aids can be briefly explained as follows: If the sound from the hearing aids is not perceived as very high, the hearing aids will be insufficient. But with the in-ear implant, sound waves are converted into electrical energy and transmitted to the auditory nerve in the ear. Thus, the patient with hearing loss perceives the sounds. Hearing aids are not placed surgically, the cochlear implant is surgically placed in the ear. Cochlear implant devices are worn if hearing aids do not benefit.