Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Serotonin? What Does Serotonin Do?
Index
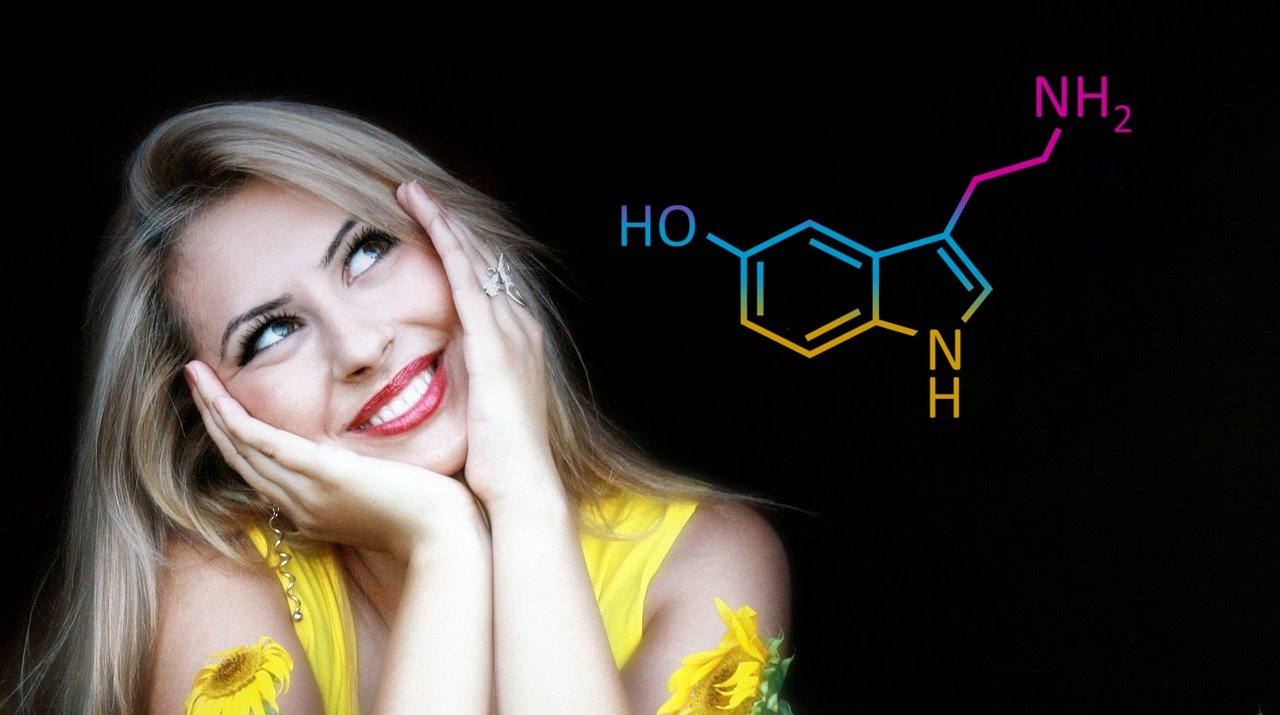
What is Serotonin?
Happiness Hormone Benefits
What Does Serotonin Do?
Low Serotonin Levels
Causes of Low Serotonin
High Serotonin Levels and Serotonin Syndrome
Symptoms of Serotonin Excess
5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), also known as serotonin hormone, is a chemical secretion that has many functions in the human body. It is also known as the happiness hormone among the people because it plays an important role in providing happiness. Serotonin, which is in the digestive system, blood platelets and central nervous system, has other functions as well as providing happiness. In the continuation of this article, you can find answers to all your questions about serotonin, such as “what is serotonin”, “what is the hormone of happiness”, “what does serotonin do”.
What is Serotonin?
Serotonin, which plays an important role in many tasks in the human body, is actually a neurotransmitter, but it is also known as a hormone because it also acts as a hormone. Serotonin carries messages between nerve cells in the brain (central nervous system) and nerve cells in the body (peripheral nervous system), and thus fulfills its duties. Serotonin is produced in the brain and intestines. Serotonin produced in the intestines makes up 90% of the serotonin produced in the whole body. Serotonin is found in the cells lining the gastrointestinal tract (digestive system). From here, serotonin enters the circulatory system and is absorbed by the platelets.
Happiness Hormone Benefits
10% of the serotonin produced in the body is serotonin produced in the brain. Serotonin cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, meaning that serotonin produced in the gut cannot reach the brain. Therefore, the brain must produce the serotonin it needs. Drugs used in the treatment of psychological diseases related to serotonin deficiency in the brain do not directly give serotonin to the body, they can generally increase the level of serotonin. Serotonin is formed with tryptophan, an essential amino acid. Essential amino acids cannot be produced in the body and must be obtained from the diet. For this reason, foods containing tryptophan must be taken from the outside in order to produce serotonin in the body. Tryptophan is generally found in foods such as meat, dairy products, eggs, and nuts.

What Does Serotonin Do?
Serotonin plays an important role in the fulfillment of many psychological and physiological functions in the body. It aids in physiological functions such as sleep, recovery, and digestion. It is also important in regulating mood. Some of the psychological and physiological functions that serotonin plays an important role in are as follows:
Mood: Serotonin is thought to be a mood stabilizer and plays an important role in regulating feelings such as happiness and anxiety. For this reason, when serotonin, known as the happiness hormone, is at normal levels, one can feel more focused, more emotionally balanced, happier and calmer. Serotonin deficiency can be associated with depression, anxiety and other mood disorders. Many drugs used in the treatment of such mental problems usually aim to increase the level of serotonin in the brain. It is thought that drugs from the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) group, which can be used in depression, anxiety and other mood disorders, affect mood disorders by increasing serotonin activity in the brain.
Digestion and bowel movements: Serotonin can also help control the movements and functions of the intestines, the part of the body where it is most produced. It can play a role in protecting the gut as well as controlling bowel functions. Intestines can increase the release of serotonin, and thus the amount, in order to get rid of foods or toxic products that will harm the body faster through digestion. Serotonin can also reduce appetite.
Bone metabolism and health: Serotonin level can play a role in bone health. If the serotonin produced in the intestines is too high, the bones may weaken. With weakening of the bones, bone fractures and osteoporosis can occur.
Sleep quality: Sleep is regulated by a group of neurotransmitters, including serotonin. Serotonin, together with another neurotransmitter dopamine, plays an important role in sleep quality. In other words, your sleep duration and the efficiency you get from your sleep can be regulated by these two neurotransmitter substances. Serotonin also plays a role in the transition to REM sleep. The brain also needs serotonin in the production of melatonin, also known as the sleep hormone.
Nausea: Nausea can be triggered when more serotonin is produced in the intestines than can be digested.
Blood clotting and wound healing: Serotonin is stored in platelets in the blood and this serotonin is released by platelets when any injury occurs in the body. Serotonin released from platelets slows blood flow by constricting blood vessels, which in turn affects clot formation. In this respect, serotonin may play a role in blood coagulation and wound healing.
Sexual health: Serotonin plays a role in sexual desire and controlling sexual functions. It is thought that this may be the reason for the side effects related to sexual functions of drugs that affect serotonin levels.
Low Serotonin Levels
Although studies have shown that low serotonin is associated with many disorders, the role of serotonin is still not fully understood. Serotonin levels in the blood can be measured, but since the serotonin circulating in the blood is not derived from the brain, but from the digestive system, its low level is not used for diagnostic purposes. For this reason, doctors may use the symptoms existing in the patient, not the laboratory findings, in order to diagnose serotonin deficiency. Some symptoms of serotonin deficiency that may be helpful in diagnosing serotonin deficiency include:
Mood changes, anxiety, depression, anxiety disorders
obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)
Panic attack
sleep problems
Dementia and memory problems
suicidal behavior
sexual dysfunctions
chronic pain
Problems with digestion and metabolism
movement problems
Problems with blood coagulation and wound healing
Migraine
Causes of Low Serotonin
Experts do not know the exact cause of low serotonin levels. However, he thinks that certain factors may cause low serotonin levels. Some factors that can be associated with low serotonin levels include:
chronic stress
Problems with nutrition
digestive problems
Less exposure to natural light and sunlight
genetic factors
Hormone changes
Some drugs used
Age-related health and brain changes
lack of physical activity
Low or decreased serotonin receptors
Problems with the digestion or absorption of serotonin
A doctor should be consulted first regarding the treatment of low serotonin levels. Your doctor can detect if there is a problem with your serotonin level by listening to your complaints. When your doctor sees a problem, he can make various treatment recommendations to increase your serotonin level related to your problem and prescribe drugs that increase the level of serotonin. Some methods that can increase the level of serotonin that your doctor may also suggest are:
exercising
Diet
Taking advantage of bright sunlight
Meditation
High Serotonin Levels and Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome is a serious reaction that occurs when too much serotonin builds up in the body, usually with medication or supplements. Serotonin syndrome is also known as serotonin toxicity.
Using different prescription drugs together
To use supplements or herbal products that affect serotonin levels at the same time, together with drugs that affect serotonin levels,
Starting a new drug that affects the serotonin level,
Using a drug that affects the serotonin level more than necessary,
Increasing the dose of a drug that has been used before and affects the serotonin level, by the doctor,
Many factors, such as illegal drugs, can cause serotonin syndrome.
Symptoms of Serotonin Excess
Excess serotonin accumulated in the body can cause various mild or severe symptoms. These symptoms can affect the brain, muscles, and other parts of the body. In some cases, an excess of serotonin can even lead to death. For this reason, if you are experiencing symptoms of serotonin excess, you should immediately contact a health care provider. Symptoms of serotonin excess include:
Mild symptoms: Nervousness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, tremor
Moderate symptoms: Agitation, restlessness, muscle twitches, cramps, muscle stiffness, sweating, tremors, dilated pupils and abnormal eye movements
Severe symptoms: Confusion or loss of consciousness, abnormally high heart rate, high fever (higher than 38.5 degrees Celsius), high blood pressure, seizures, fainting, coma
If you think you have a problem with your serotonin level, do not neglect to apply to the nearest health institution.