Table of Contents
ToggleOrganic Matter Destruction in Plants
Plants also need free energy to carry out various vital activities and to continue their lives. This free energy is provided by the burning of organic nutrients obtained through photosynthesis by the plant itself, ie oxidation. The free oxygen of the air is used to burn the food, but some living things breathe without using oxygen.
Aerobic respiration (Oxygen respiration)
It occurs when plants take the free oxygen from the air, break down the nutrients and give carbon dioxide to the air by the living thing.
Anaerobic respiration (Oxygen-free respiration)
It is the respiration performed by using only the oxygen in the tissues of the plants, without using the free oxygen of the air.
Stages of Oxygen Respiration
In respiration, organic foods with bound energy must be burned and broken down into less complex compounds in order to provide the free energy required for the life events of the living thing from the bound chemical energy made by the plant by photosynthesis. For this reason, respiration is also called the “breakdown of organic matter”. Aerobic respiration occurs in three phases.
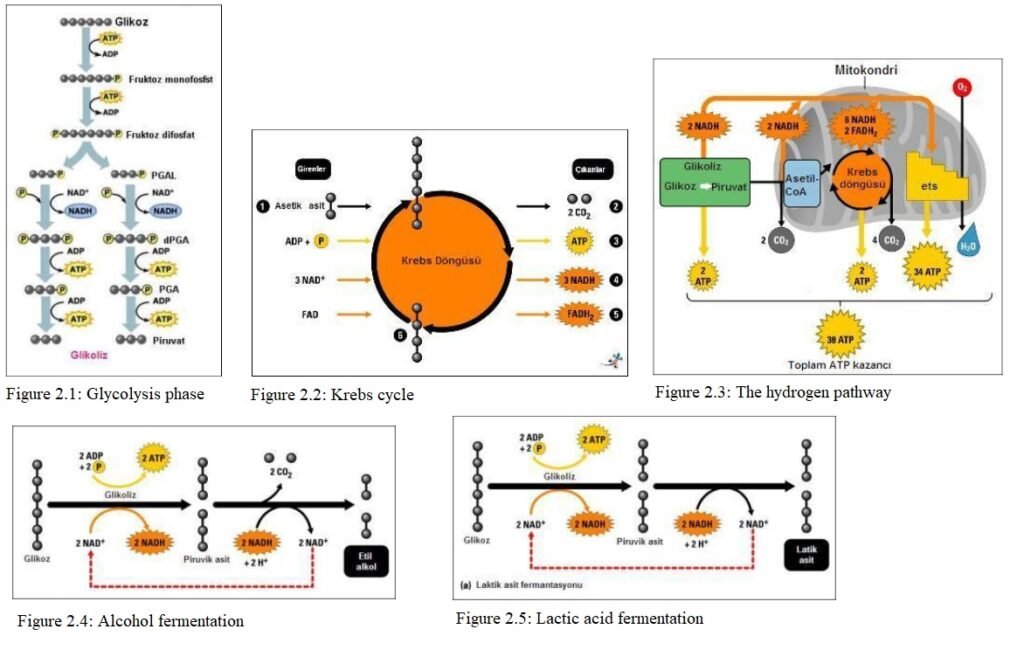
Glycolysis Stage
Organic substances that usually participate in the reaction in respiration are sugars with 6 carbons. If simple sugars are not available, other foods are used. These foods are converted into simple sugars and then participate in the glycolysis phase.
It takes place in the cytoplasm. For glucose to undergo aerobic respiration reactions, it must first be activated. ATPs in the environment are used. It is the breakdown of glucose in the cytoplasm by enzymes to pyruvate. As a result, 2 moles of NADPH2 and 2 ATP are produced.
Glucose 2Pyruvate + 2ATP+ 2NADPH2
Krebs Cycle
It takes place within the mitochondrial organelle. In the glycolysis phase, glucose is broken down to pyruvate. One mole of CO2 and 2H are removed from pyruvate and acetyl CoA (acetyl-coenzyme-A) is formed. Acetyl CoA is the basic substance that will start the Krebs cycle. As a result, ATP, CO2, FADH2, NADH are formed.
Hydrogen Path
The path followed by the hydrogens in glucose to combine with oxygen to form H2O is called the hydrogen path. The hydrogen pathway is the part of respiration where energy is generated. The hydrogen atoms separated during the breakdown of glucose are captured by NAD and FAD. These captured hydrogens are transferred to the ETS (electron transport system).
The high-energy electrons of hydrogen captured by NAD and FAD release their energy into the system. During this time, most of the energy is lost in the form of heat. Most of the remaining energy is used to add phosphate to ADP to produce ATP. Obtaining ATP in this way is called oxidative phosphorylation.
The hydrogen atom and electron that loses their energy combine with O2 at the end of the ETS to form H2O.
Factors Affecting Respiratory Intensity
Different plants and organs have different respiratory rates. Generally, leaves are the most vigorous respiration organs. As a rule, between plant organs according to the excess of respiratory rate; There is an order in the form of leaves, roots and stems. Respiration rates vary in different tissues. The most vigorous respiration occurs in the cambial tissue. As a rule, the factors affecting the respiratory rates of plants and tissues are of two parts. These:
genetic factors
metabolic events
environmental factors
Oxygen density and temperature.
Comparison of Respiration and Photosynthesis
Respiration and photosynthesis are two opposite metabolic events. The table below shows the differences between the two events.
Photosynthesis
– Occurs only in green plant cells.
– Occurs only under light.
– H2O and CO2 are used.
– O2 is released.
– Solar energy chemical
– There is an increase in weight.
– Organic foods are made.
– O2 and organic matter are synthesized.
Respiratory
– Occurs in all plant cells.
– It lasts a lifetime in the light and in the dark.
– Organic matter and O2 are used.
– Water and CO2 come out.
– Chemical energy to work energy
– Weight reduction occurs.
– Organic foods are destroyed.
– H2O, CO2 and ATP are synthesized.
Enzymes
Various special substances in protein quality that catalyze (accelerate) the reactions related to various metabolic events, are not included in the final product, are called enzymes. Enzymes consist of two parts:
– The part from the protein is the apoenzyme
– Non-protein part coenzyme or cofactor
Enzymes working in plants are grouped into three important groups according to the places where they work. These:
– Secretion enzymes (in insectivorous plants)
– Endoenzymes (work in cell vacuoles)
– Dermoenzymes (works in plasma)
