Table of Contents
ToggleCell Science
Cell Structure and Functions
The cell is the smallest structural unit of the plant. Cells; Regardless of their shape, size and structure, they carry out vital events such as feeding, producing and using energy, transferring hereditary characteristics to offspring. Cells; consists of cell membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus.
Cell Membrane
All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that separates the cell from the external environment. Cell membrane; It has a lively, selective and permeable structure. There are no holes in the cell membrane.
– The functions of the cell membrane are as follows;
– It separates the cell from the external environment.
– Protects the cell.
– It gives shape to the cell.
– Exchanges items.
– Plant cells have a cell wall above the membrane.
– Cell wall: It is lifeless, thick and permeable; consists of cellulose. As the plant cell ages, substances such as wood pulp and fungal pulp accumulate on the cell wall and thickening is achieved. There are passages in the thickened cell wall that allow the exchange of substances.
– Gateways: As the cells age and the wall thickens, the exchange of substances between the cells becomes impossible. In this case, the cells lose their vitality. The non-death of cells depends on the passages in the wall. Passages occur as a result of wall thickening.
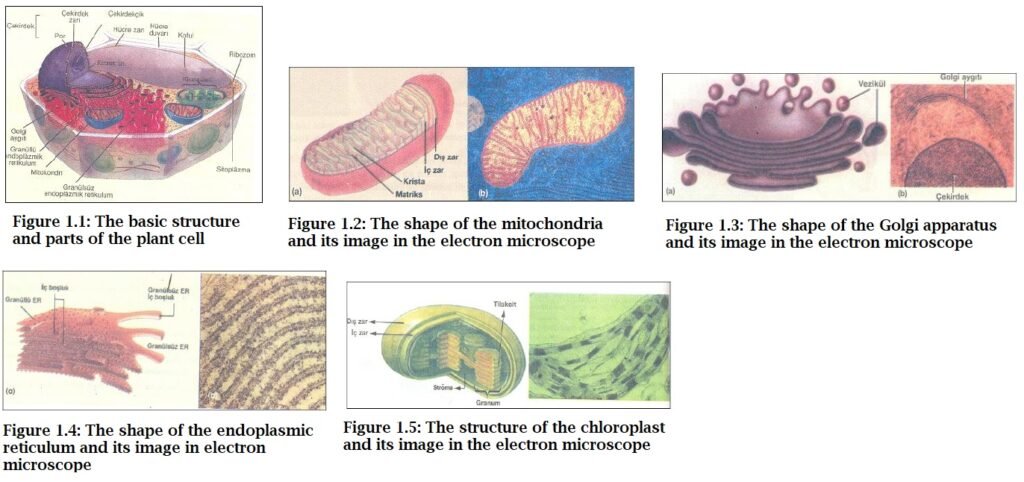
Cytoplasm and Organelles
The cytoplasm fills between the cell membrane and the nucleus. The cytoplasm contains organic and inorganic substances. Organic substances in the cytoplasm; structural proteins, nucleotides, enzymes, carbohydrates, fats, hormones and vitamins. 75–90% of the cytoplasm is water, but it cannot pass through the membrane. In addition to water, mineral substances are also found in the cytoplasm. Numerous enzymatic reactions take place in the cytoplasm.
Organelles that enable life activities in the cell are found in the cytoplasm.
Organelles found in plant cells are:
– Ribosome: It is the smallest organelle of the cell. It is not surrounded by dice. It consists of protein and RNA. It is also found in mitochondria and chloroplast organelles. Ribosomes are produced in nucleoli within the cell nucleus. Its job is to synthesize proteins.
– Mitochondria: It is a double membrane organelle. The inner membrane folds inward to form crystals (protrusions). The outer membrane is smooth. Mitochondria contain DNA and RNA. The job of mitochondria is to produce energy for cell activity. It is less in green plants than in animal cells.
Golgi body: It is formed by the accumulation of tubes and pillows formed by thin membranes. It is very common in secretory cells. It changes the structure of the protein produced in the ribosome and turns it into a secretory substance. The cellulose in the plant is secreted by the Golgi body.
Duties:
– Synthesizes and packages the secretion substance.
– It synthesizes fatty substances.
– Combines protein and carbohydrates to make glycoproteins.
– It participates in the structure of the cell membrane.
– It provides vacuole formation.
– It creates an intermediate lamella in cell division and ensures the division of the cytoplasm.
The endoplasmic reticulum is a system of canaliculi extending between the cell membrane and the nucleus.
Duties:
– It provides the transport of proteins to the necessary places in the cell.
– It prevents acidic and basic reactions from affecting each other in the cell.
Vacuum: They are structures surrounded by a thin membrane in the cytoplasm and filled with a special fluid. Vacuoles are small and numerous in young plant cells. In old plant cells, they are large and their number is less.
Duties:
– It forms crystals by combining the toxic wastes released as a result of metabolism with inorganic salts and accumulates them in its structure.
– It regulates the osmotic pressure of the cell.
– Plastids: Protoplasmic bodies with important metabolic functions found in the cytoplasm. It is divided into three in terms of form and function. These:
– Chloroplast: It is the plastid that gives the plant its green color. It is the organelle where photosynthesis takes place in the cell. chloroplast; It is found in young branches, leaves, raw vegetables and fruits. As the fruit ripens, the green chloroplast turns into a chromoplast later on. It is not found in flower and stem cells.
Chloroplast is an organelle with a double membrane. It contains ribosome organelle, DNA and RNA. He can match himself. chloroplast; It consists of two parts, the granum and the stroma.
– Granum: It is the part where chlorophyll pigment is found. Chlorophyll pigment absorbs sunlight and provides energy conversion.
The stroma is the liquid part that fills the chloroplast. It contains photosynthesis enzymes.
– Chromoplast: Organelle carrying different color pigments. Color pigments; yellow, orange and red. Chromoplast gives flowers and fruits their color other than green.
– Leucoplasts: They are found in the organs of the plant such as roots, underground stems and seeds that do not receive light. Starch stores fat and protein. It is colorless.
Cell
It has an oval appearance. It is located in the center of the cell. It provides the transmission of hereditary characteristics from one generation to another by the regulation and management of metabolic activities (division, growth, etc.) in the cell.
The core is analyzed in four parts.
– Nuclear membrane: It separates the cytoplasm and the nucleus. It has holes called pores on it. It is double storey.
– Core juice: It fills the core. It contains water, RNA, nucleotides and enzymes.
– Nucleolus: It contains RNA and proteins in its structure. The nucleolus plays an important role in protein synthesis.
– Chromosomes: Chromosomes are found in a certain number, shape and structure in all members of a living species. They are structures that carry genes with a unit of heredity. All the vital activities of the cell are governed by genes.
Cell Proliferation
Cells reproduce by dividing. Division varies according to the characteristics of the cell. The rate of cell division can vary from plant to plant, as well as according to different tissues and organs of the same plant. Cell division allows the plant to grow and develop, as well as the regeneration of worn-out tissues and organs. There are two types of cell division.
Mitotic division
Mitosis allows plants to grow. It is seen at the root tips of the stem and branch tips. In addition, mitosis is required for the regeneration of worn-out tissues and organs. At the end of mitosis, the volume of the cell decreases and the number of cells increases.
Mitosis occurs in two stages. These:
– Interphase (preparation) phase: In the interphase (preparation) phase;
– The energy to be used during the division is prepared.
– Protein is synthesized for spindle fibers.
– Chromosomes replicate.
– Nuclear replication and cytoplasm division phase: This division takes place in four phases. These phases are; prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
– Prophase: Nuclear membrane and nucleolus melt away. Chromatin threads become chromosomes. They are shortened. Most are thickened.
– Metaphase: Spindle fibers are formed. Pairing chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. Chromosomes can be counted at this stage.
– Anaphase: Spindle fibers shorten. Pairing chromosomes move to poles on spindle fibers. In the last stage, the spindle fibers start to disappear from the center.
– Telophase: Chromosomes are pulled completely to the poles. Chromatin turns into thread. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus are formed. This completes the kernel mapping.
After nuclear replication is complete, the cytoplasm divides into two. In some cells, the cytoplasm is not divided. In this case, multinucleated cells are formed.
Cytoplasmic division occurs differently in plants and animals. Cytoplasm division in plant cell; Since the membrane is adherent to the cell wall, after the anaphase stage, the wall-forming substance collects in the center of the cytoplasm and forms the intermediate chamber. This wall material divides the cytoplasm in two from the inside out.
Meiosis
meiosis; It occurs while the egg cell is forming in the flower and pollen is forming on the head of the male organ. The purpose of this division is to halve the number of chromosomes. If there were only mitosis in living cells, the number of chromosomes would double in the daughter cell. This means that it is a living being that does not resemble its parents.
Meiosis occurs in two major phases. These:
– Meiosis stage: This stage is also divided into four stages in itself. These; prophase-1, metephase-1, anaphase -1, telophase-1.
– Prophase 1: Chromatin threads shorten and thicken. Similar chromosomes from the mother and father come together. Sister chromatids appear next to each chromosome. Spindle threads are formed. The nuclear membrane melts.
– Metaphase 1: Chromotids line up in the center of the cell in bundles of four.
– Anaphase 1: As the spindle fibers shorten and thicken, the sister chromatids move to the poles together. The cytoplasm begins to condense.
– Telophase 1: Chromosomes are completely pulled to the poles. A nuclear membrane forms around them. Thus, two haploid cells are formed.
– Second meiosis stage: This stage is also divided into four stages in itself. These; prophase-2, metaphase-2, anaphase-2, telophase-2.
Similar to mitosis. When meiosis ends, 4 cells with haploid chromosomes are formed. When two reproductive cells with haploid chromosomes belonging to the male and female living thing unite, a cell with a diploid chromosome is formed. This cell is called a zygote.
Differences in mitosis and meiosis cell division:
– Mitosis occurs in most normal body cells (somatic). Meiosis occurs in reproductive cells (gametes).
– Terate is not formed in mitosis. In meiosis, tetrads (quadruple chromatids) are formed.
– Chromosome number remains constant in mitosis (2n). During meiosis, the number of chromosomes decreases by half (from diploid 2n to haploid n).
– Only one division takes place in mitosis (nuclear and cytoplasm division). In meiosis, two divisions occur in succession (two nuclear divisions).
– Two daughter cells are formed in mitosis. In meiosis, 4 daughter cells are formed.
The daughter cells formed in mitosis are identical to each other and to the parent cell. Daughter cells that occur in meiosis may not resemble the parent cell because they carry different combinations of chromosomes.